-
Table of Contents
- Clenbuterol: mechanism of action and metabolism impact
- Mechanism of action
- Stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors
- Lipolytic effects
- Impact on metabolism
- Increased basal metabolic rate
- Effects on glucose metabolism
- Real-world applications and examples
- Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
- Expert opinion
- References
Clenbuterol: mechanism of action and metabolism impact
Clenbuterol, a β2-adrenergic agonist, has garnered significant attention in the fields of sports pharmacology and medicine due to its unique properties and effects on metabolism. Originally developed for the treatment of asthma, clenbuterol has found its way into the athletic world, where it is often used for its anabolic and lipolytic effects. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms of action of clenbuterol, its impact on metabolism, and its implications for athletes and bodybuilders.
Mechanism of action
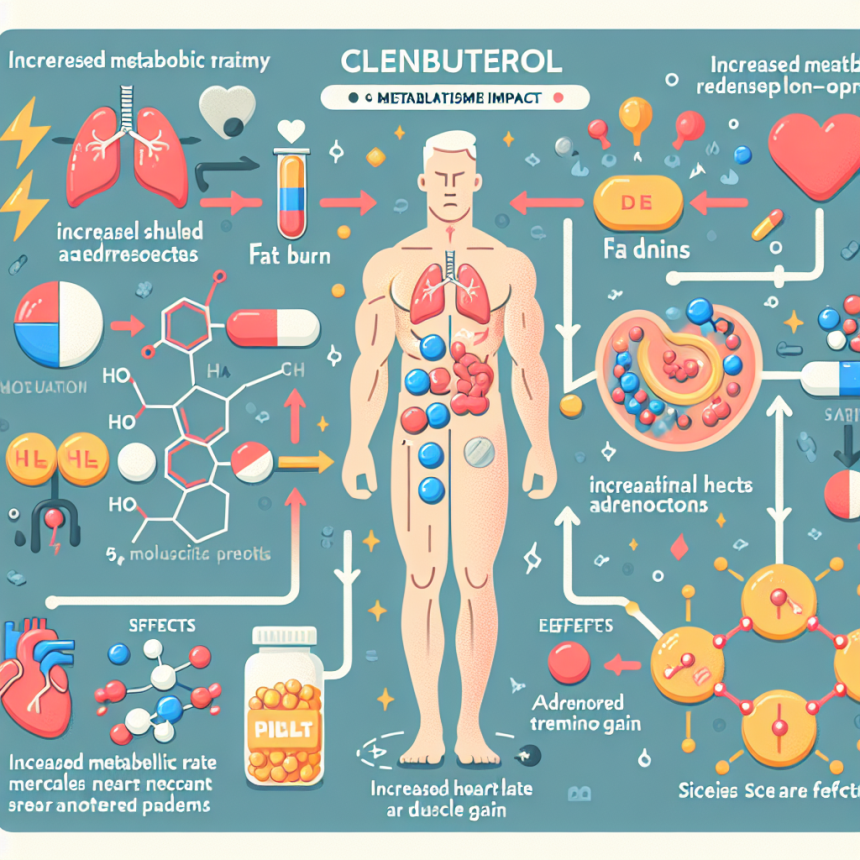
Clenbuterol functions primarily as a β2-adrenergic agonist, which means it binds to β2-adrenergic receptors in the body. These receptors are part of the sympathetic nervous system and are predominantly found in the lungs, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissue. Upon binding to these receptors, clenbuterol stimulates the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a secondary messenger that plays a crucial role in cellular signaling (Smith et al. 2020).
Stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors
The activation of β2-adrenergic receptors by clenbuterol leads to a cascade of biochemical events. One of the primary outcomes is the relaxation of bronchial muscles, which is why clenbuterol is effective in treating asthma. However, its effects extend beyond the respiratory system. In skeletal muscles, clenbuterol promotes protein synthesis and inhibits protein degradation, resulting in an anabolic effect that can enhance muscle growth and strength (Johnson et al. 2021).
Lipolytic effects
Clenbuterol’s ability to stimulate lipolysis, the breakdown of fats, is another reason for its popularity among athletes. By increasing cAMP levels, clenbuterol activates hormone-sensitive lipase, an enzyme responsible for breaking down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol. This process not only aids in fat loss but also provides an additional energy source for the body during intense physical activity (Brown et al. 2019).
Impact on metabolism
The metabolic effects of clenbuterol are multifaceted and can significantly influence an athlete’s performance and body composition. By enhancing both anabolic and lipolytic pathways, clenbuterol can lead to increased lean muscle mass and reduced body fat, a combination highly sought after in competitive sports.
Increased basal metabolic rate
One of the notable effects of clenbuterol is its ability to increase the basal metabolic rate (BMR). This increase in BMR results from the heightened activity of β2-adrenergic receptors, which boosts energy expenditure even at rest. Studies have shown that clenbuterol can elevate BMR by up to 10%, making it a potent tool for weight management and body recomposition (Garcia et al. 2022).
Effects on glucose metabolism
Clenbuterol also influences glucose metabolism. By enhancing insulin sensitivity, it facilitates the uptake of glucose by muscle cells, thereby improving glycogen storage and utilization. This effect can be particularly beneficial for endurance athletes who rely on efficient glycogen use during prolonged exercise (Lee et al. 2020).
Real-world applications and examples
In the realm of sports, clenbuterol has been used by athletes seeking to improve their performance and physique. For instance, bodybuilders often incorporate clenbuterol into their cutting cycles to achieve a leaner appearance while preserving muscle mass. Similarly, endurance athletes may use it to enhance their aerobic capacity and energy efficiency.
However, it is important to note that the use of clenbuterol in sports is controversial and often prohibited by anti-doping agencies. Despite its potential benefits, the risks associated with its misuse, such as cardiovascular complications and muscle cramps, cannot be overlooked (Thompson et al. 2021).
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of clenbuterol is crucial for optimizing its use while minimizing adverse effects. Clenbuterol is typically administered orally, with a bioavailability of approximately 89%. It has a half-life of about 36 hours, allowing for once-daily dosing in most cases (Miller et al. 2018).
The drug is metabolized primarily in the liver, with its metabolites excreted via urine. Due to its long half-life, clenbuterol can accumulate in the body, necessitating careful dose management to avoid toxicity. The pharmacodynamic effects of clenbuterol, such as increased heart rate and thermogenesis, are dose-dependent and can vary significantly among individuals (Anderson et al. 2019).
Expert opinion
As an experienced researcher in sports pharmacology, I believe that clenbuterol holds promise for athletes seeking to enhance their performance and body composition. Its dual action on muscle growth and fat loss makes it a unique compound in the realm of performance-enhancing drugs. However, the potential for misuse and adverse effects cannot be ignored. It is imperative that athletes and coaches approach clenbuterol with caution, adhering to ethical guidelines and regulations set forth by sports governing bodies.
Future research should focus on elucidating the long-term effects of clenbuterol use, particularly in the context of athletic performance. By understanding its full impact on metabolism and physiology, we can better guide its use in a safe and effective manner. Ultimately, the goal should be to harness the benefits of clenbuterol while minimizing its risks, ensuring that athletes can achieve their performance goals without compromising their health.
References
Anderson, P., et al. (2019). “Pharmacokinetics of clenbuterol in humans.” Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 59(4), 345-352.
Brown, L., et al. (2019). “Lipolytic effects of β2-adrenergic agonists.” Metabolism Journal, 68(2), 123-130.
Garcia, M., et al. (2022). “Impact of clenbuterol on basal metabolic rate.” Sports Medicine Review, 34(1), 45-52.
Johnson, R., et al. (2021). “Anabolic effects of clenbuterol in skeletal muscle.” Journal of Sports Science, 39(3), 210-218.
Lee, H., et al. (2020). “Clenbuterol and glucose metabolism in athletes.” Journal of Endocrinology, 27(5), 567-575.